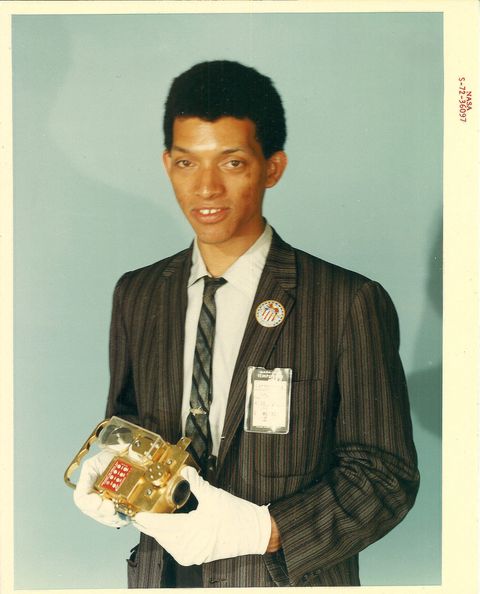
GM – FBF – Today’s American Champion was an African American inventor, physicist, engineer and space scientist. Carruthers perfected a compact and very powerful ultraviolet camera/spectrograph for NASA to use when it launched Apollo 16 in 1972. He designed it so astronauts could use it on the lunar surface, making all adjustments inside their bulky space suits.Upon instructions from Carruthers, they used the camera to record the Earth’s outermost atmosphere, noting its variations, and also mapped portions of the far-ultraviolet sky recording stars and galaxies, and the gaseous media between them. In 1970, sending his instruments aboard Aerobee sounding rockets, he had demonstrated that molecular hydrogen exists in the interstellar medium.Among numerous citations and awards, in 2003, Carruthers was inducted into the National Inventor’s Hall of Fame. He received an honorary doctorate for Engineering from Michigan Technological University, and in 2013 the 2012 National Medal for Technology and Invention from President Barack Obama.Today in our History – George Robert Carruthers (October 1, 1939 – December 26, 2020) was born. Scientist George Carruthers created inventions, such as the ultraviolet camera, or spectograph, which was used by NASA in the 1972 Apollo 16 flight, revealing the mysteries of space and the Earth’s atmosphere. Scientist George Carruthers built his first telescope at the age of 10. He earned his Ph.D. in aeronautical and astronautical engineering at the University of Illinois in 1964 and began working at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory. His telescope and image converter was used to identify molecular hydrogen in space and his ultraviolet camera/spectograph was used by Apollo 16 during the flight to the moon. Scientist George Carruthers was born on October 1, 1939, in Cincinnati, Ohio, the eldest of George and Sophia Carruthers’ four children. George Carruthers, Sr. was a civil engineer with the U.S. Army Air Corps, and encouraged his son’s early interests in science. By the age of 10, the young Carruthers had constructed his own telescope with cardboard tubing and mail-order lenses he bought with money he earned as a delivery boy.Carruthers’ father died when the boy was only 12. After his death, the family moved to Chicago, where Sophia went to work for the U.S. Postal Service. Despite the emotional setback, Carruthers continued pursuing science. As one of only a handful of African-Americans competing in Chicago’s high school science fairs, he won three awards, including first prize for a telescope that he designed and built.In 1957, Carruthers graduated from Chicago’s Englewood High School and entered the engineering program at the University of Illinois’ Champaign-Urbana campus. While an undergraduate, Carruthers focused on aerospace engineering and astronomy. After earning his bachelor’s degree in physics in 1961, Carruthers stayed on at the University of Illinois, earning his master’s in nuclear engineering in 1962, and his Ph.D. in aeronautical and astronautical engineering in 1964.In 1964, he went to work for the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory as a National Science Foundation postdoctoral fellow. Two years later he became a full-time research physicist at the NRL’s E. O. Hurlburt Center for Space Research. Please research more about this great American Champion and share it with your babies. Make it a champion day!
Month: October 2021
GM – FBF – Today’s North American Champion was a Canadian track and field sprinter and physical education teacher
GM – FBF – Today’s North American Champion was a Canadian track and field sprinter and physical education teacher. He won a bronze medal at the 1964 Olympics in Tokyo and set a total of seven world records over the course of his career.Today in our History – September 30, 1940 – “Harry” Winston Jerome was born.Harry Jerome was born in Prince Albert, Saskatchewan, the son of Harry Vincent Jerome and Elsie Ellen Howard, and moved to North Vancouver, British Columbia, at age 12. His grandfather was John Howard, an American-born railway porter who represented Canada in the 1912 Summer Olympics. Harry’s sister, Valerie Jerome, was also an Olympian who competed for Canada at the 1960 Summer Olympics in Rome.Jerome competed at the university level for Bill Bowerman at the University of Oregon. He was a member of the Canadian track and field team at the 1960, 1964, and 1968 Summer Olympics, winning 100 meter bronze in 1964. Jerome wore his University of Oregon sweats, rather than the contemporary practice of an official national outfit for all Olympic appearances, to warm up for the Olympic 100 meters in Tokyo. He won the gold in the 1966 British Empire and Commonwealth Games.During his career, Jerome set a total of seven world records, including tying the 100 meter record at 10.0 seconds in 1960, equaling the mark established a month earlier by Germany’s Armin Hary. Later he tied the world record for the 100-yard dash at 9.3 seconds (1961), making Jerome one of the few athletes to own both the 100 yard and 100 meter world record simultaneously.Jerome was a member of the University of Oregon 4 × 100 m relay team that tied the world record of 40.0 seconds in 1962; during the 1962 season Harry ran 9.2s at the 100-yard dash 2 times. In 1966 he again tied a world record with a 9.1 time in the 100 yard. From 1963 to 1966 he held or equaled four world records concurrently. He remains the only man to have held the 100 yard world record with 3 different times & is the oldest 100y world record holder – 25 years old; the youngest is Houston McTear at 9.0s he was 18 years old. Jerome never owned the 100y or 100m WR solely but matched his contemporaries.Jerome continued to sprint successfully until the late 1960s, despite suffering an injury so severe at the Perth Commonwealth Games in 1962 that doctors initially believed he would be crippled for life.[citation needed]Jerome received a bachelor’s degree in physical education from the University of Oregon in 1964 and taught with the Richmond School Board (1964–65) and then with the Vancouver School Board (1965–68). In 1968, he received a master’s in physical education from Oregon.After retiring from athletics in 1969, Jerome was invited by Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau to help create Canada’s new Ministry of Sport. Jerome held a number of senior positions in the ministry but resigned over the government’s cancellation of a large public-private partnership he had negotiated with Kellogg’s to promote youth participation in athletics. During the 1980s, Jerome headed the Premier’s Sport Award program in British Columbia.Jerome died of a brain aneurysm on December 7, 1982, at the age of 42, in North Vancouver.In 1970, Jerome was made an Officer of the Order of Canada. The following year he was inducted into Canada’s Sports Hall of Fame. Jerome was posthumously inducted into Canada’s Walk of Fame in 2001 and was named a Person of National Historical Significance in 2010.In 1984, the Labatts International Track Classic Pre-Olympic meet was renamed the Harry Jerome International Track Classic. The meet is held annually at Swangard Stadium in Burnaby, British Columbia. The Harry Jerome Sports Complex in North Vancouver, one block from North Vancouver High School where he first went out for track in 1958, and the Harry Jerome Sports Centre, home to the Burnaby Velodrome, are named after Jerome, as are the weight room at the University of Oregon and the track and field stadium in Prince Albert.The Stanley Park sea wall in Vancouver is graced with a 2.7-metre (9 ft) bronze statue of Jerome. The annual Harry Jerome Awards, the national awards dinner for Canada’s black community organized by the Black Business and Professionals Association (BBPA), is named after him.Another meet, called the Harry Jerome Indoor Games was created in 2011. It is held at the Richmond Olympic Oval, once used for Speed Skating events at the 2010 Vancouver Olympics, but now a multi-purpose sports facility. The meet is mainly attended by high school students representing lower mainland clubs, as well as some university student-athletes, and younger athletes.On September 30, 2019, Google celebrated Harry Jerome’s 79th birthday with a Google Doodle.Production began in April 2009 on a feature-length biographical documentary entitled Mighty Jerome. Directed by Charles Officer and produced by the National Film Board of Canada (NFB) in Vancouver, the film was inspired by Fil Fraser’s book on Jerome, entitled Running Uphill.NFB producer Selwyn Jacob had approached Officer — along with four other directors — in 2007 with idea of making a documentary about Jerome. Officer’s proposal was selected by Jacob and the NFB, despite the fact that he had never directed a documentary before.The black and white film uses archival footage, interviews and dramatizations to explore Jerome’s life and career. Officer recreated museum installations in Toronto, Edmonton and Vancouver to interview Jerome’s contemporaries and family members. Jerome’s sister Valerie refused to participate in the film due to objections over his portrayal in Fraser’s book. The film premiered at the Vancouver International Film Festival on October 8, 2010.Jerome’s 100 meter bronze medal performance at the Tokyo 1964 Summer Olympics is captured in the documentary film Tokyo Olympiad (1965) directed by Kon Ichikawa. Slow motion close-up footage of Jerome (along with other athletes) preparing for the race begins at the 26-minute mark and then the race is shown in its entirety at full speed. Research more about this great North American Champion and share it with your babies. Make it a champion day!